We are proud to present the results of a Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) study for the SPEX recycling process, conducted by CE Delft. CE Delft carried out this LCA for three different waste streams (HDPE, laminates, medical tubes) with the aim of determining the carbon footprint and comparing it with reference processes for plastic production and waste processing.
The LCA was conducted from both a product perspective, comparing the SPEX recycling process with fossil-based production processes, and a waste perspective, comparing it with current waste processing methods. The LCA is based on the mass and energy balances of the conceptual design of the commercial 20 kT installation and the tests conducted in their pilot and lab facility at their Plant One Rotterdam location.
The results are excellent and confirm previous LCA findings for dissolution conducted for the Province of South Holland, TNO and CE Delft.
- SPEX distinguishes itself from fossil-based production and other recycling technologies with its excellent LCA results;
- There is no difference in the findings between the product perspective and the waste perspective;
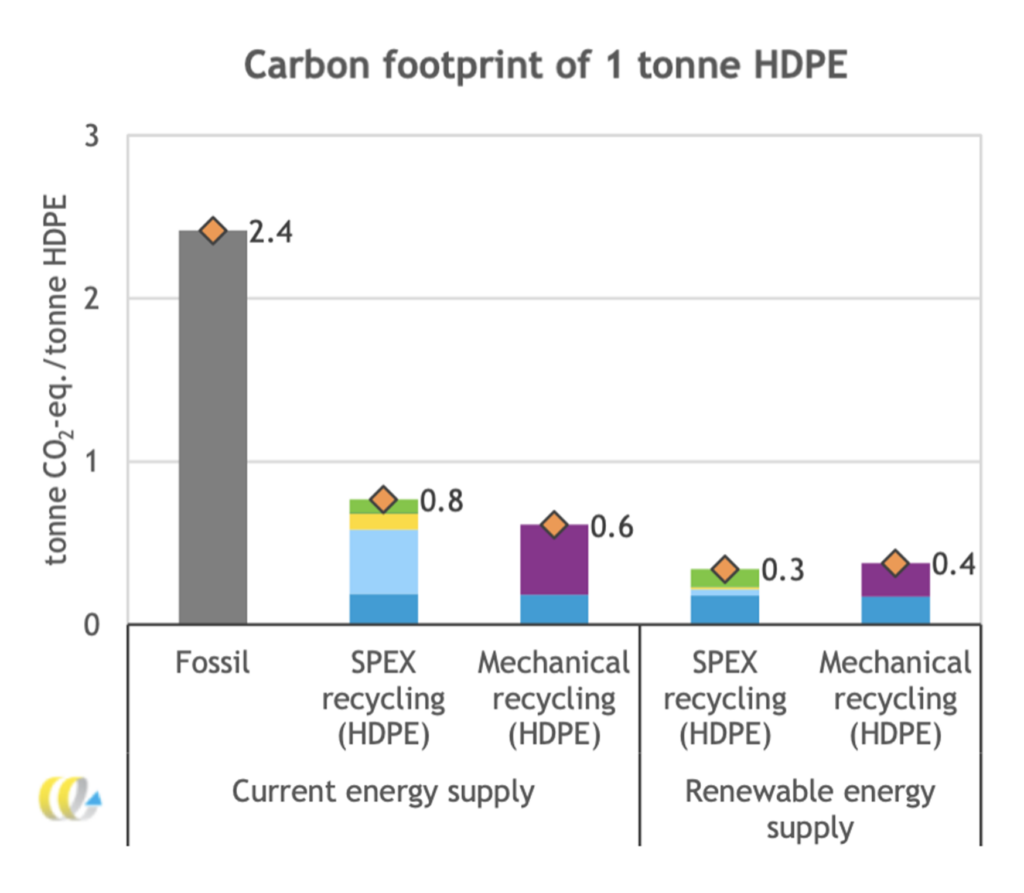
- The carbon footprint of HDPE produced via SPEX is significantly lower (a reduction of 1.6 t CO2-eq./t) than the carbon footprint of fossil-based HDPE;
- The LCA of SPEX is comparable to that of mechanical recycling, especially when renewable energy is used;
- The positive LCA outcomes apply to all three investigated streams;
- The LCA results are even better when renewable energy is used, and/or when combined with sustainable recycling of the PET residue, such as with Ioniqa.
This LCA highlights the significant carbon footprint reduction impact as an important differentiator compared to incineration, fossil-based virgin production and chemical recycling.
The summary of the public report is available here.